
Therefore \(x = 4\,and\,x = 5\) are the roots of quadtratic equations. \((x - 4)\) and \((x - 5)\) are multiplying to give zero, therefore one of these brackets must be equal to zero. There are four different methods used to solve equations of this.

When solving quadratic equations, we can use two. A quadratic equation in is an equation that may be written in the standard quadratic form if. Before you select the method that you will use to solve a quadratic, you must use inverse operations to get the equation to equal. Standard Form of Quadratic Equations: ax2 + bx + c 0. When factorised this is \((x - 4)(x - 5) = 0\). This is because in each of these equations the greatest exponent of any variable is 2. In other words, where does the parabola cut the x-axis?Īs a graph cuts the axis when the y coordinate is zero, then we substitute \(y = 0\) into the quadratic equation and use algebra to solve. Firstly, let us find where it is equal to zero: (x+2) (x3) 0. Check by inserting your answer in the original equation. The discriminant b24ac>0 so, there are two real. x2 x 6 has these simple factors (because I wanted to make it easy): (x+2) (x3) < 0. Solving Quadratic Equations Put all terms on one side of the equal sign, leaving zero on the other side.

For problems 4 8 solve the quadratic equation by completing the square. Example 1: Find the Solution for x2+8x+50, where a 1, b -8 and c 5, using the Quadratic Formula. When a question asks you to 'solve' a quadratic equation, this means that you are to find the roots of the quadratic. Section 2-6 : Quadratic Equations - Part II. Look at the National 4 factorising section before continuing.
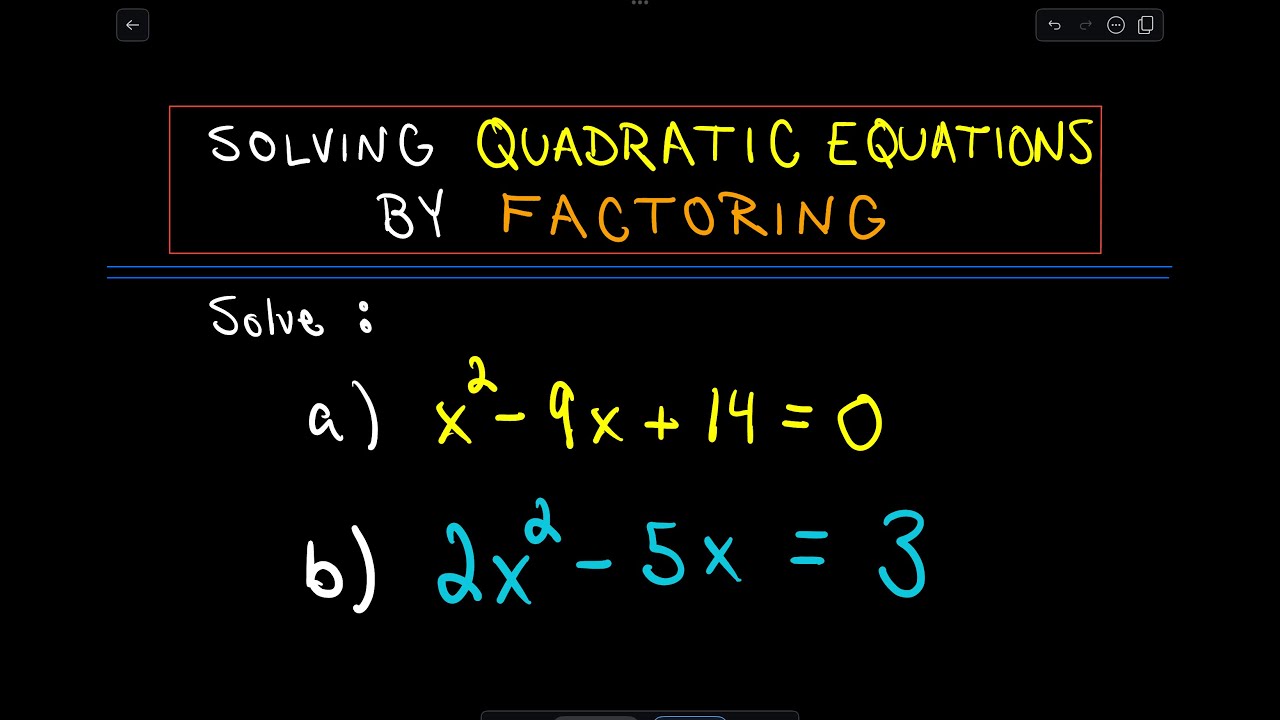
Quadratic equations can be solved by the following methods:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
